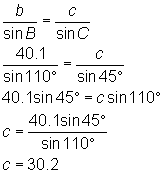Law of Sines: Examples
Let’s take a look at some examples using the Law of Sines.
Example 1:
Given 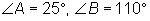 and b = 40.1, solve triangle ABC (round your answer to the nearest tenth).
and b = 40.1, solve triangle ABC (round your answer to the nearest tenth).
The first step is always to draw a diagram (this diagram is not drawn to scale):
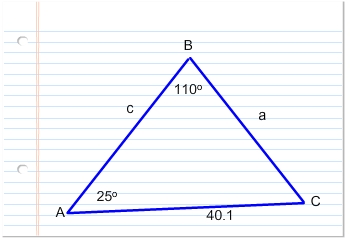
You can find the measure of angle C by remembering that the angles of any triangle add up to 180°. You can write the following equation:
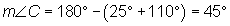
You can then find sides a and c by using the Law of Sines:
To find a:
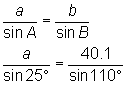
Cross-multiply to get:
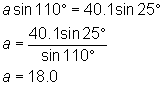
To find c: